Bone disorders
Adequate amounts of vitamin D throughout one's life - in combination with exercise, proper nutrition, calcium, and magnesium - are necessary for building up and maintaining bones and preventing bone loss. Vitamin D is needed to properly absorb calcium. Studies have shown that low levels of vitamin D and insufficient sunlight exposure (fewer than 20 minutes per day) are associated with osteoporosis. Calcium, together with vitamin D, has been shown to help heal bone fractures from osteoporosis and decrease the risk of future bone breaks. In addition, vitamin D has demonstrated a beneficial effect on muscle function and strength and thereby reduces the risk of falling. Moreover, vitamin D is well known to protect against ‘rickets’ and ‘osteomalacia’, diseases of severe vitamin
deficiency.
Cancer
Studies in test tubes have indicated that vitamin D may have anti-cancer effects, while clinical study findings on vitamin D and specific cancers such as colorectal cancer have been inconsistent. However, some studies have shown strong evidence that high doses of vitamin D supplements may reduce the risk of colorectal cancer. In addition, some population studies have suggested that supplementation with vitamin D may improve survival rates in those with a history of breast cancer. Other studies indicated that vitamin D3 supplementation might be effective in treating skin cancer. However, this research is still in the experimental stages.
Autoimmune diseases
Research suggests that vitamin D deficiency or a low vitamin D status may be linked to an increased risk of developing autoimmune diseases, overactive immune responses of the body attacking its own cells and organs. Clinical studies evaluating the use of vitamin D for some forms of arthritis (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis) have found vitamin D to have preventive effects. Observational data has suggested that vitamin D from foods and sunlight may help protect against multiple sclerosis (MS), a disease in which the body's immune response attacks a person's brain and spinal cord. Research has shown that supplementing infants and children with high doses of vitamin D may protect against the development of type 1 diabetes, a disease in which the body’s immune system destroys the insulin-producing cells.
Cardiovascular disease and High blood pressure
Data from clinical studies have suggested a link between low levels of vitamin D and high blood pressure. Moreover, low vitamin D status (as measured by the 25(OH)-vitamin D plasma level) is thought to be independently associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality or a higher risk of a heart attack.
Other disorders
Although the information is limited, studies have suggested that vitamin D supplementation may also be helpful to prevent Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD), a form of depression that occurs during the winter months because of lack of sunlight, and tuberculosis, an infectious disease.
Medical Blog
Translate
Do you like my Blog
Most Trending
-
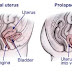
Prolapsi vaginal është një fryrje dhe rënie e mureve vaginale. Kjo ndodh kur indet mbështetëse të pelvisit dobesohen. Mungesa e mbeshtetj...
-
Me tension të ulet të gjakut kuptojmë kur gjaku në arteriet tuaja është më i ulet sesa vlerat referente. Sigurisht presion i ulet i gjaku...
-
Qendra amerikane për kontrollin e sëmundjeve rekomandon vaksinimin e mëposhtëm për fëmijët 0-6 vjet: Vaksina e Hepatitit B (HepB): mos...
-
Introduction Folliculitis may progress to form subcutaneous inflammatory abscesses known as furuncles, or boils, which usually drain and r...
-
Dhimbjet në gju mund të shkaktohen nga dëmtimet e papritura, një dëmtim i tepruar ose nga një gjendje themelore të tilla si artriti. T...
BMI Calculator
Life Traffic
Best Metabolic Rate
Labels
Dukagjin Zeqiraj. Powered by Blogger.
Featured
Featured
Subscribe
Click
Videos
Total Pageviews
Top 5 in Week
-
Prolapsi vaginal është një fryrje dhe rënie e mureve vaginale. Kjo ndodh kur indet mbështetëse të pelvisit dobesohen. Mungesa e mbeshtetj...
-
Etiology: Acne vulgaris (or acne) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects areas with the greatest concentration of sebaceous glan...
-
Complete blood count Reference Values RBC Parameters (Conventional...
-
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory disease with no known cure. It is associated with significant psychosocial morbidity and decre...
Top 5 In Month
-
Prolapsi vaginal është një fryrje dhe rënie e mureve vaginale. Kjo ndodh kur indet mbështetëse të pelvisit dobesohen. Mungesa e mbeshtetj...
-
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory disease with no known cure. It is associated with significant psychosocial morbidity and decre...
-
In 1987, holiday heart syndrome was described from a study of 24 patients who presented to the hospital during the holiday season with at...
-
Qendra amerikane për kontrollin e sëmundjeve rekomandon vaksinimin e mëposhtëm për fëmijët 0-6 vjet: Vaksina e Hepatitit B (HepB): mos...
-
Etiology: Acne vulgaris (or acne) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects areas with the greatest concentration of sebaceous glan...
Don't Copy
Most Trending
-
Prolapsi vaginal është një fryrje dhe rënie e mureve vaginale. Kjo ndodh kur indet mbështetëse të pelvisit dobesohen. Mungesa e mbeshtetj...
-
Me tension të ulet të gjakut kuptojmë kur gjaku në arteriet tuaja është më i ulet sesa vlerat referente. Sigurisht presion i ulet i gjaku...
-
Qendra amerikane për kontrollin e sëmundjeve rekomandon vaksinimin e mëposhtëm për fëmijët 0-6 vjet: Vaksina e Hepatitit B (HepB): mos...
-
Introduction Folliculitis may progress to form subcutaneous inflammatory abscesses known as furuncles, or boils, which usually drain and r...
-
Dhimbjet në gju mund të shkaktohen nga dëmtimet e papritura, një dëmtim i tepruar ose nga një gjendje themelore të tilla si artriti. T...
Contact Form
© Copyright
Dukagjin Zeqiraj











0 comments:
Post a Comment